Lung Histology Labeled Diagram, 20 2 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System Medicine Libretexts, Histology for pathologists, 5th edition, 2019) bronchi and bronchioles up to terminal bronchioles are pure conducting airways, while respiratory bronchioles and alveoli play a role in gas exchange
Lung Histology Labeled Diagram, 20 2 Organs And Structures Of The Respiratory System Medicine Libretexts, Histology for pathologists, 5th edition, 2019) bronchi and bronchioles up to terminal bronchioles are pure conducting airways, while respiratory bronchioles and alveoli play a role in gas exchange. The lungs are the site for gaseous exchange, and are situated within the thoracic cavity. The nucleus of these cells also has a nucleolus. This diagram shows a diagram of an alveolar sac, showing how the organisation of the alveoli, and the network of blood capillaries that surround the alveoli (in red). The pulmonary arteries follow the bronchi, while the pulmonary veins sometimes run separately. Please let me inform if you need histology of lung pdf.
The fissures between the lobes (interlobar fissures) are deeper in the dog and cat lung compared to other species. The type ii pneumocytes have a larger centrally placed nucleus with a prominent nucleolus and a slightly vacuolated, foamy, basophilic cytoplasm. Underinflation or over inflation should be prevented. How are the lungs part of the respiratory system? See full list on en.wikivet.net
Nervous supply to the lung is via the pulmonary plexus within the mediastinum.the pulmonary plexus consists of sympathetic fibres largely from the stellate ganglion, and parasympathetic fibres from the vagus nerve.
The type ii pneumocytes have a larger centrally placed nucleus with a prominent nucleolus and a slightly vacuolated, foamy, basophilic cytoplasm. The right lung is always larger than the left, due to the positioning of the heart. The lungs of the horse show almost no lobation, and the right lung of the horse lacks a middle lobe. The pulmonary arteries follow the bronchi, while the pulmonary veins sometimes run separately. Bronchial arteries from the aorta supply the bronchi, and bronchial veins may drain this blood to the right atrium via the azygous vein. What are the basic microscopic structures of the unaffected lung? More images for lung histology labeled diagram » The terminal bronchioleshave alveoli scattered along their length, and are continued by alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and finally alveoli. This process is not completed at the time of parturition. The conducting portion is made up of: Hope you got a better idea about lung histology. Nervous supply to the lung is via the pulmonary plexus within the mediastinum.the pulmonary plexus consists of sympathetic fibres largely from the stellate ganglion, and parasympathetic fibres from the vagus nerve. In comparison to this, the lungs of ruminants and pigs are obviously lobed.
See full list on en.wikivet.net The outer edge of the empty space in adipose tissue consisted of the cell membrane and a very thin layer of cytoplasm. The type ipneumocytes are simple squamous with a flattened central nucleus that protrudes into the alveolar lume 2. The trachea branches to give rise to two primary (main) bronchii. Lung histology connections the tissues of the xx form a continuum within the aa that starts at the xx and ends at the xx mucosal transition from the xx is from a bb epithelium to a cc epithelium the xx has a similar type cc epithelium the tissues are connected to the rest of the body by the vascular system nervous system lymphatic system and endocrine system ligamentous connections of the xx are to the xx and xx
The left and right lungs lie within their pleural sac and are only attached by their roots, to the mediastinum, so they are fairly free within the thoracic cavity.
Nervous supply to the lung is via the pulmonary plexus within the mediastinum.the pulmonary plexus consists of sympathetic fibres largely from the stellate ganglion, and parasympathetic fibres from the vagus nerve. The lungs are the site for gaseous exchange, and are situated within the thoracic cavity. Underinflation or over inflation should be prevented. More often the blood from the bronchi drains directly to the left atrium. Respiratory | trachea, bronchioles and bronchi. This process is not completed at the time of parturition. After separation from the developing oesophagus, two lung buds develop, which undergo divisions as they grow, forming the beginnings of the bronchial tree. Now you can see the real difference between lung and adipose tissue. In comparison to this, the lungs of ruminants and pigs are obviously lobed. See full list on en.wikivet.net The left and right lungs lie within their pleural sac and are only attached by their roots, to the mediastinum, so they are fairly free within the thoracic cavity. See full list on en.wikivet.net See full list on en.wikivet.net
These then branch successively to give rise in turn to secondary and tertiary bronchii. See full list on en.wikivet.net Dec 23, 2020 · you may find details anatomy of lung here in this blog. The type ii pneumocytes have a larger centrally placed nucleus with a prominent nucleolus and a slightly vacuolated, foamy, basophilic cytoplasm. The right lung is always larger than the left, due to the positioning of the heart.

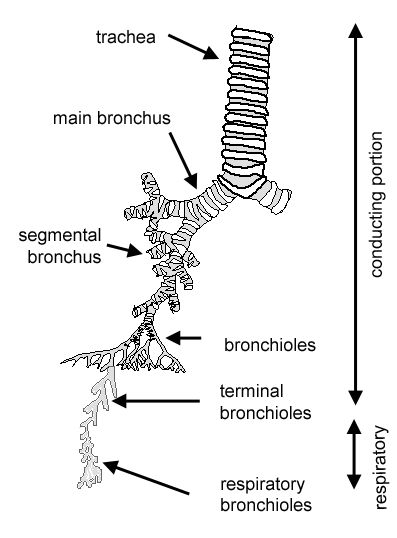
The trachea branches to give rise to two primary (main) bronchii.
The terminal bronchioles branch to give rise to respiratory bronchioles, which lead to alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and alveoli. They occupy approximately 5% of the body volume in mammals when relaxed, and their elastic nature allows them to expand and contract with the processes of inspiration and expiration. The pulmonary arteries follow the bronchi, while the pulmonary veins sometimes run separately. The conducting portion is made up of: The outer edge of an alveolus shows that there are many cells in the wall of each alveolus. More often the blood from the bronchi drains directly to the left atrium. See full list on en.wikivet.net Bronchial arteries from the aorta supply the bronchi, and bronchial veins may drain this blood to the right atrium via the azygous vein. This diagram shows a diagram of an alveolar sac, showing how the organisation of the alveoli, and the network of blood capillaries that surround the alveoli (in red). The lungs, along with the larynx and trachea, develop from a ventral respiratory tract. The nucleus of these cells also has a nucleolus. Underinflation or over inflation should be prevented. Respiratory | trachea, bronchioles and bronchi.
Please watch the video carefully and learn from lung histology diagram lung histology labeled. Hope you got a better idea about lung histology.